Page 13 - QuakerMillDam
P. 13
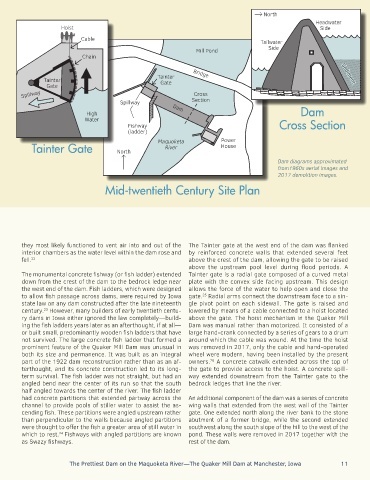
North
Headwater
Hoist Side
Cable
Tailwater
Side
Mill Pond
Chain
Bridge Sediment
Tainter
Tainter Gate
Gate
Spillway Cross
Spillway Section
Dam
High Dam
Water
Fishway Cross Section
(ladder)
Tainter Gate North Maquoketa Power
House
River
Dam diagrams approximated
from1960s aerial images and
2017 demolition images.
Mid-twentieth Century Site Plan
they most likely functioned to vent air into and out of the The Tainter gate at the west end of the dam was flanked
interior chambers as the water level within the dam rose and by reinforced concrete walls that extended several feet
fell. 22 above the crest of the dam, allowing the gate to be raised
above the upstream pool level during flood periods. A
The monumental concrete fishway (or fish ladder) extended Tainter gate is a radial gate composed of a curved metal
down from the crest of the dam to the bedrock ledge near plate with the convex side facing upstream. This design
the west end of the dam. Fish ladders, which were designed allows the force of the water to help open and close the
to allow fish passage across dams, were required by Iowa gate. Radial arms connect the downstream face to a sin-
25
state law on any dam constructed after the late nineteenth gle pivot point on each sidewall. The gate is raised and
century. However, many builders of early twentieth centu- lowered by means of a cable connected to a hoist located
23
ry dams in Iowa either ignored the law completely—build- above the gate. The hoist mechanism in the Quaker Mill
ing the fish ladders years later as an afterthought, if at all— Dam was manual rather than motorized. It consisted of a
or built small, predominantly wooden fish ladders that have large hand-crank connected by a series of gears to a drum
not survived. The large concrete fish ladder that formed a around which the cable was wound. At the time the hoist
prominent feature of the Quaker Mill Dam was unusual in was removed in 2017, only the cable and hand-operated
both its size and permanence. It was built as an integral wheel were modern, having been installed by the present
part of the 1922 dam reconstruction rather than as an af- owners. A concrete catwalk extended across the top of
26
terthought, and its concrete construction led to its long- the gate to provide access to the hoist. A concrete spill-
term survival. The fish ladder was not straight, but had an way extended downstream from the Tainter gate to the
angled bend near the center of its run so that the south bedrock ledges that line the river.
half angled towards the center of the river. The fish ladder
had concrete partitions that extended partway across the An additional component of the dam was a series of concrete
channel to provide pools of stiller water to assist the as- wing walls that extended from the west wall of the Tainter
cending fish. These partitions were angled upstream rather gate. One extended north along the river bank to the stone
than perpendicular to the walls because angled partitions abutment of a former bridge, while the second extended
were thought to offer the fish a greater area of still water in southwest along the south slope of the hill to the west of the
which to rest. Fishways with angled partitions are known pond. These walls were removed in 2017 together with the
24
as Swazy fishways. rest of the dam.
The Prettiest Dam on the Maquoketa River—The Quaker Mill Dam at Manchester, Iowa 11